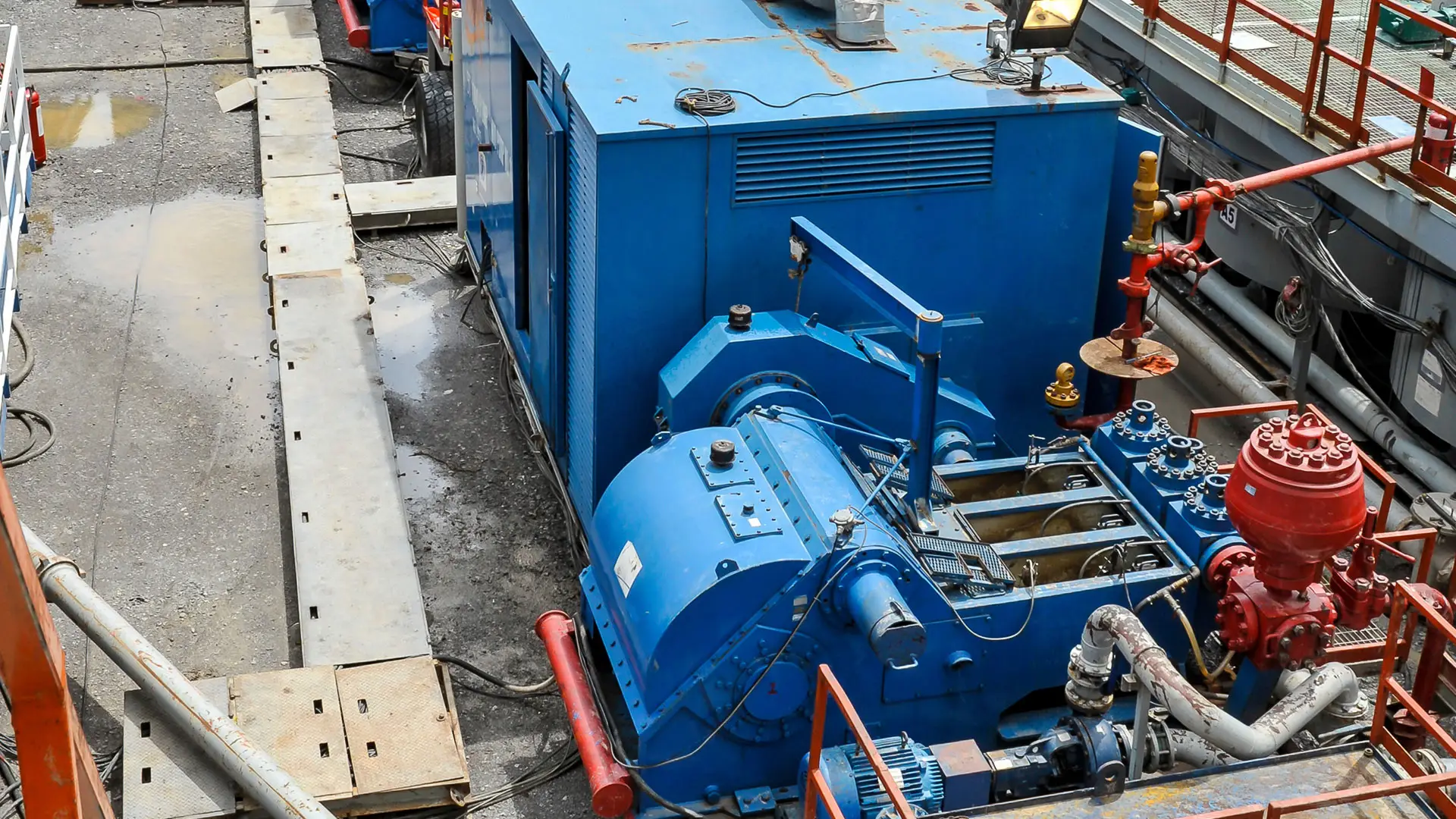
Dredging pumps are essential components in industries like mining, construction, environmental remediation, and marine dredging. These powerful pumps handle abrasive materials such as sand, silt, gravel, and slurry, making them vulnerable to wear and tear. Proper maintenance is critical to ensuring consistent performance, minimizing downtime, and extending the lifespan of your dredging pump.
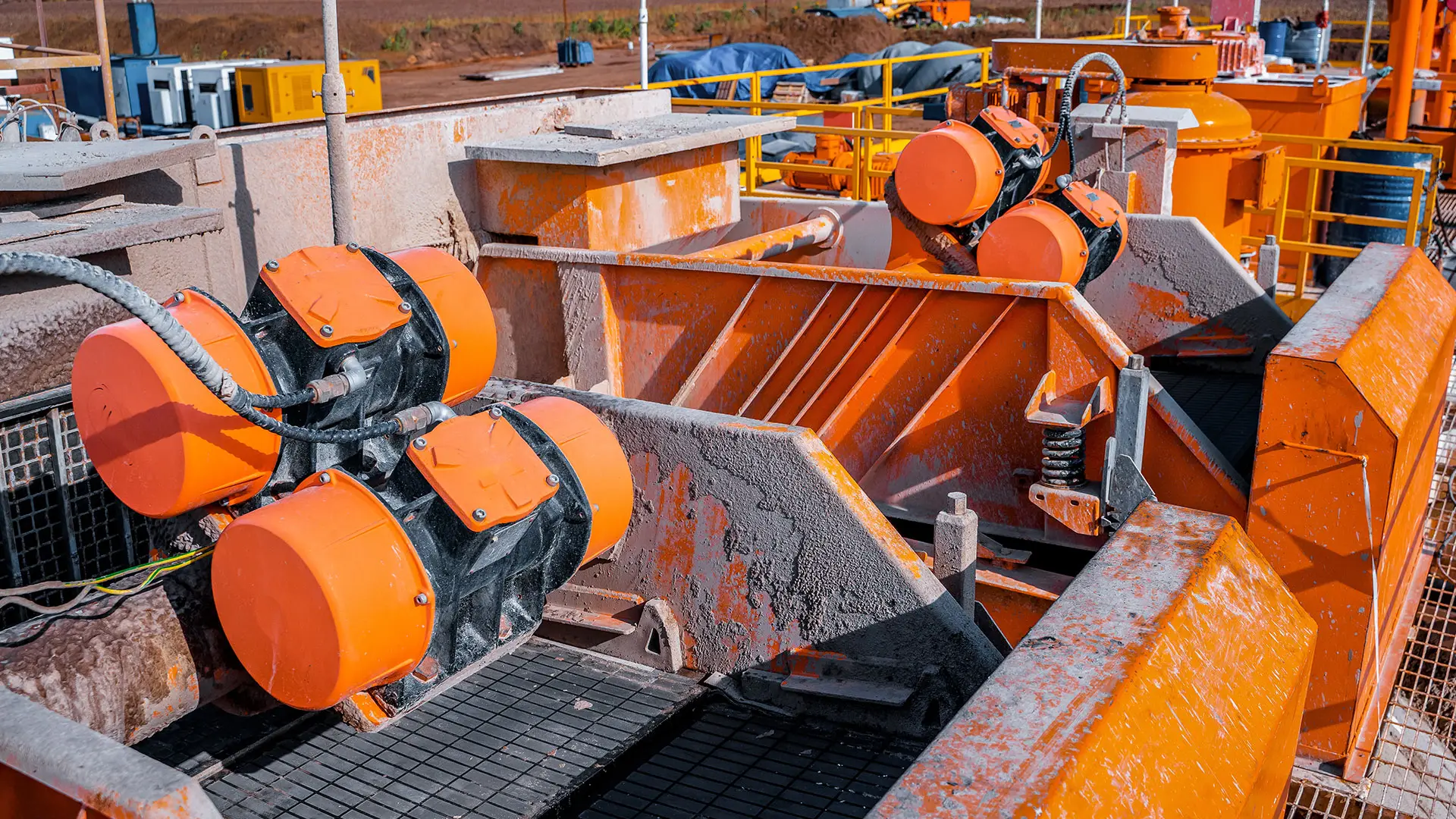
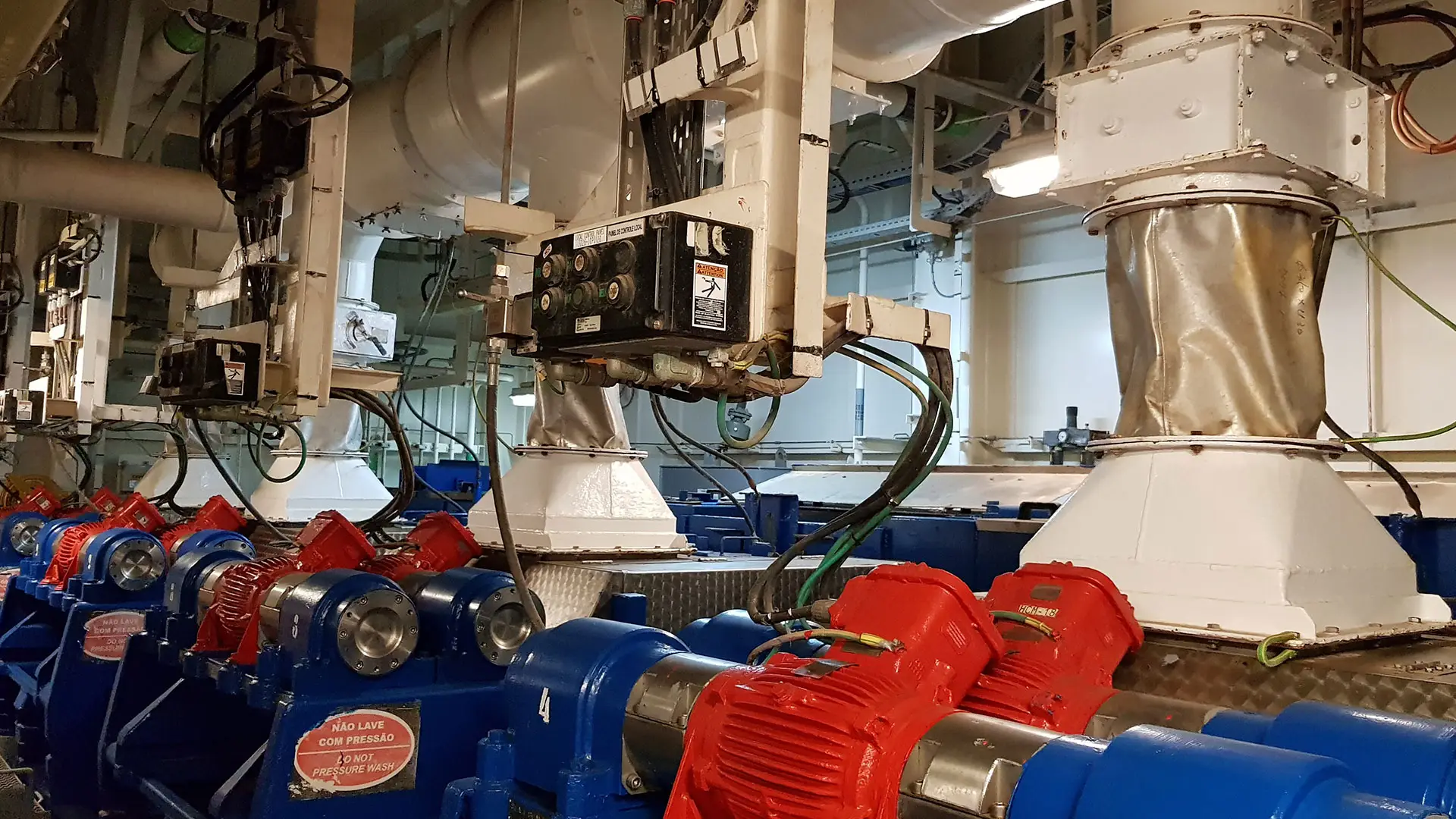
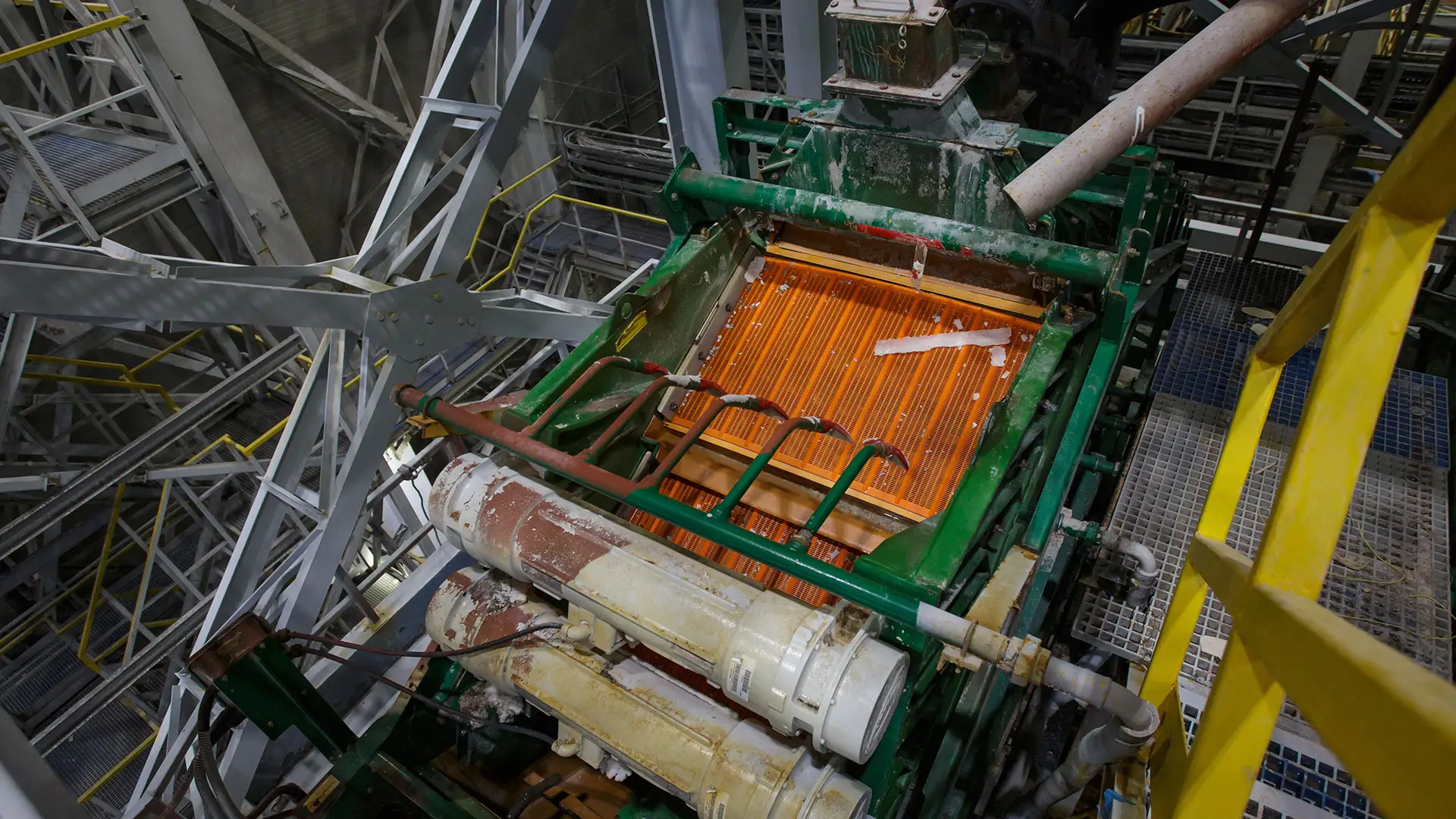
Shale shakers play a crucial role in separating solids from liquids in dredging operations, and maintaining the shale shaker part is equally important for overall system efficiency. A worn or damaged shale shaker part can reduce the performance of the linear motion shale shaker, leading to increased sediment buildup and reduced pump efficiency. Regularly inspecting and replacing shale shaker parts will help avoid costly breakdowns and improve overall dredging performance.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll cover the key components of dredging pumps, including how to maintain shale shakers and ensure optimal linear motion shale shaker performance. We’ll also explore common causes of wear and damage, essential maintenance practices, advanced monitoring strategies, and best practices for maximizing pump lifespan.
Proper maintenance of dredging pumps and shale shakers involves routine inspections, lubrication, cleaning, and replacement of worn components like the impeller and casing. Monitoring vibration levels and conducting real-time condition-based analysis can help prevent unexpected failures. By implementing these maintenance strategies, you can extend the lifespan of your dredging pump and maintain consistent operational efficiency.
Whether you’re managing a large dredging project or using a smaller industrial pump, understanding the role of shale shaker parts and maintaining them properly will significantly enhance performance and reduce downtime.
Understanding Dredging Pump Components
Before diving into maintenance strategies, it’s important to understand the key components of a dredging pump and how they function together to handle heavy-duty materials efficiently.
A. Key Parts of a Dredging Pump
A dredging pump is a complex piece of machinery composed of several critical parts that work together to handle abrasive materials like sand, silt, and gravel:
- Impeller – The impeller is the heart of the pump. It rotates at high speed to create centrifugal force, which moves slurry and solids through the pump.
- Casing – The casing houses the impeller and directs the flow of the slurry. Its design is essential for handling abrasive materials without excessive wear.
- Shaft and Bearings – The shaft connects the impeller to the motor, and the bearings support the shaft to ensure smooth rotation and reduce vibration.
- Suction and Discharge Pipes—Suction pipes draw in slurry, while discharge pipes expel it. Proper alignment and pressure control are key to efficient operation.
- Seals and Liners – Seals prevent leakage, while liners protect the casing from abrasive wear.
Shale shakers are also vital in dredging systems as they separate solids from liquids before the slurry reaches the pump. A worn shale shaker part can reduce efficiency and increase pump wear. Regular maintenance of the linear motion shale shaker and timely replacement of shale shaker parts will enhance the performance and lifespan of your dredging pump.
B. How Dredging Pumps Work
Dredging pumps rely on centrifugal force to transport sediment and slurry. The rotating impeller creates a low-pressure zone that draws the slurry into the suction pipe. The centrifugal force pushes the slurry through the discharge pipe, ensuring consistent flow and pressure — both of which are essential for preventing cavitation and wear.
Common Causes of Dredging Pump Wear and Damage
Dredging pumps operate under harsh conditions, making them vulnerable to various forms of damage. Understanding these causes will help you prevent costly failures and extend the lifespan of your equipment.
A. Abrasion and Erosion
Pumping abrasive materials like sand, gravel, and silt can cause significant wear on internal components:
- High-density slurries create friction against the impeller and casing, gradually reducing efficiency and causing material loss.
- Abrasive particles wear down the pump’s internal surfaces, leading to increased maintenance needs.
- Using hardened or coated materials for impellers and casings can help resist abrasion and prolong component life.
- A worn shale shaker part can also increase the pump’s wear by allowing larger abrasive particles to pass through, causing internal damage. Regular inspection and replacement of shale shaker parts can reduce pump wear.
B. Cavitation
Cavitation occurs when air bubbles form in the pump due to low suction pressure or improper priming:
- When these bubbles collapse, they create shock waves that damage the impeller and casing.
- Misaligned suction lines or incorrect suction head height are common causes of cavitation.
- Maintaining proper suction pressure and avoiding dry starts can prevent cavitation.
- If the linear motion shale shaker isn’t functioning properly, it may allow excessive air or debris into the pump, increasing the likelihood of cavitation.
C. Corrosion
Exposure to saltwater, chemicals, and acidic materials can corrode metal components:
- Corrosion weakens the structural integrity of the pump and increases wear.
- Coating components with corrosion-resistant materials, such as stainless steel or special alloys, can reduce corrosion damage.
- Flushing the pump with fresh water after handling corrosive materials is essential to prevent long-term damage.
D. Improper Operation
Human error is a leading cause of premature pump failure:
- Running the pump dry can destroy seals and bearings.
- Incorrect motor alignment causes vibration and damage to the shaft and impeller.
- Overloading the pump increases heat and wear on internal components.
- A malfunctioning shale shaker can allow excessive solids or debris to enter the pump, clogging it and increasing stress on the impeller and casing.
- Ensuring that operators are trained on proper pump operation and maintenance is critical to reducing damage and improving longevity.
Essential Maintenance Practices
Routine maintenance is the key to extending the lifespan of your dredging pump. Following these practices will minimize wear, improve efficiency, and prevent costly breakdowns.
A. Routine Inspection and Monitoring
Regular inspections are critical for identifying and addressing issues before they escalate:
- Conduct visual inspections for cracks, leaks, and misalignments.
- Monitor pressure and flow rates to identify early signs of performance issues.
- Keep a maintenance log to track wear patterns and the lifespan of key components.
- A malfunctioning shale shaker part can lead to excessive sediment entering the pump, causing increased wear. Regularly inspect and replace shale shaker parts as needed.
B. Lubrication and Cooling
Proper lubrication reduces friction and prevents overheating:
- Bearings and seals require consistent lubrication to minimize wear.
- Overheating can lead to bearing failure, so ensure proper cooling during operation.
- Use the correct type and amount of lubricant specified by the manufacturer.
- A well-maintained linear motion shale shaker ensures proper separation of solids, reducing the load on the pump and improving lubrication performance.
C. Cleaning and Flushing
Cleaning helps prevent material buildup and corrosion:
- Remove sediment and debris from the pump after each use.
- Flush the pump with fresh water if it’s used in saltwater or chemical environments.
- A properly functioning shale shaker will reduce the amount of debris entering the pump, improving overall performance.
D. Seal and Liner Replacement
Replacing seals and liners on time prevents leaks and damage:
- Monitor seals for wear and leakage.
- Replace worn or damaged seals and liners promptly.
- Follow manufacturer guidelines for proper installation and alignment.
E. Vibration Analysis and Alignment
Addressing misalignment and imbalance reduces stress on the pump:
- Use vibration analysis tools to detect alignment issues early.
- Realign the motor and shaft as needed to prevent excessive vibration and wear.
Advanced Maintenance Strategies
Implementing advanced strategies in addition to routine maintenance can further extend the lifespan of your dredging pump and improve its overall efficiency.
A. Condition-Based Monitoring
Condition-based monitoring allows you to track performance in real time and address issues before they lead to failure:
- Install sensors to monitor pressure, temperature, and vibration continuously.
- Monitor data for signs of wear or performance issues.
- Automate alerts when performance drops below target levels to take corrective action quickly.
- If a shale shaker part is worn or malfunctioning, excessive debris can enter the pump, leading to pressure imbalances and increased wear. Replacing faulty parts promptly helps maintain stable performance.
B. Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance leverages AI and machine learning to anticipate failures and reduce downtime:
- Use AI to analyze historical data and predict when components are likely to fail.
- Schedule maintenance and part replacement before breakdowns occur.
- Refine predictive models based on real-world performance data.
- Proper monitoring of the linear motion shale shaker can prevent damage to the pump by ensuring efficient solids separation, reducing the workload on the impeller and casing.
C. Spare Parts Management
Effective spare parts management helps avoid prolonged downtime:
- Keep essential spare parts like seals, impellers, and bearings in stock.
- Establish agreements with manufacturers for fast replacement of parts.
- Ensure that replacement parts meet original manufacturer specifications.
- A malfunctioning shale shaker or a worn shale shaker part can cause damage to the pump’s internal components, having spare parts available reduces repair time and improves operational efficiency.
Best Practices to Maximize Pump Lifespan
Following best practices can significantly extend the lifespan of your dredging pump and improve operational efficiency. Consistent monitoring and proper handling of the pump are essential to prevent unnecessary wear and breakdowns.
A. Proper Startup and Shutdown Procedures
Starting and stopping the pump correctly prevents sudden stress and damage:
- Gradually increase speed and pressure during startup to avoid pressure surges.
- Ensure that suction and discharge lines are properly primed before starting the pump.
- Allow the pump to cool down properly before shutting it off to prevent overheating and thermal shock.
- A malfunctioning shale shaker part can cause improper material separation, leading to uneven pressure buildup during startup. Regular inspection and replacement of shale shaker parts help maintain consistent operation.
B. Optimal Pump Configuration
Proper configuration ensures that the pump operates within its designed parameters:
- Ensure that the pump size matches the operational requirements.
- Maintain correct motor alignment to avoid vibration and wear.
- Keep suction and discharge pressures balanced to prevent cavitation and excessive load on the impeller.
- A properly functioning linear motion shale shaker efficiently separates solids before they reach the pump, reducing the risk of clogging and pressure imbalances.
C. Operator Training
Educating operators on proper handling and maintenance improves pump longevity:
- Train operators to monitor performance and identify early signs of wear.
- Encourage proactive maintenance and regular inspections of key components, including shale shakers and other critical parts.
- Providing training on replacing a worn shale shaker part can prevent costly damage to the pump and extend its lifespan.
When to Replace or Upgrade Your Dredging Pump
Knowing when to replace or upgrade your dredging pump is essential for maintaining operational efficiency and avoiding costly downtime.
Signs of Irreversible Wear or Damage
Over time, even with proper maintenance, dredging pumps will experience wear:
- Cracked or heavily worn impellers, casings, and seals may no longer function effectively.
- Frequent leaks or pressure drops despite regular maintenance could indicate internal damage.
- A worn shale shaker part can allow excessive solids to pass through, increasing wear on the pump’s internal components and reducing overall efficiency.
Performance Decline Despite Maintenance Efforts
If the pump’s performance continues to decline after regular maintenance, it may be time to consider a replacement:
- Reduced flow rate and pressure may signal internal component failure.
- If the linear motion shale shaker is not properly separating solids, it may put additional strain on the pump, accelerating wear.
- A damaged shale shaker part can cause inconsistent material separation, leading to pump clogging and reduced efficiency.
Evaluating the Cost of Repair vs. Replacement
- If repair costs exceed 50% of the cost of a new pump, replacement is often the better option.
- Newer pumps with improved designs and upgraded shale shakers may offer better efficiency and longer lifespan, making them a more cost-effective solution.
Conclusion
Extending a dredging pump’s lifespan requires routine maintenance, advanced monitoring, and proper operating procedures. Regular inspection and maintenance of key components like the impeller, casing, and seals are essential for preventing wear, reducing downtime, and improving overall pump efficiency. Implementing condition-based and predictive maintenance strategies will further enhance pump reliability and performance.
A well-maintained shale shaker is crucial for efficient dredging operations. If a shale shaker part becomes worn or damaged, excessive solids can pass through, increasing the load on the pump and accelerating wear. Ensuring that the linear motion shale shaker operates properly helps maintain consistent material separation, reducing the risk of clogging and improving flow rates. Regularly checking and replacing shale shaker parts will minimize downtime and improve pump longevity.
Investing in proper maintenance isn’t just about avoiding failures, it’s about maximizing the return on your dredging equipment investment. A properly functioning linear motion shale shaker and well-maintained shale shakers can significantly improve dredging efficiency and reduce overall operating costs. For expert advice, professional support, or to explore high-performance dredging solutions, contact Eddy Pump today. Ensuring that your shale shakers and pumps are in top condition will help you achieve long-term operational success.